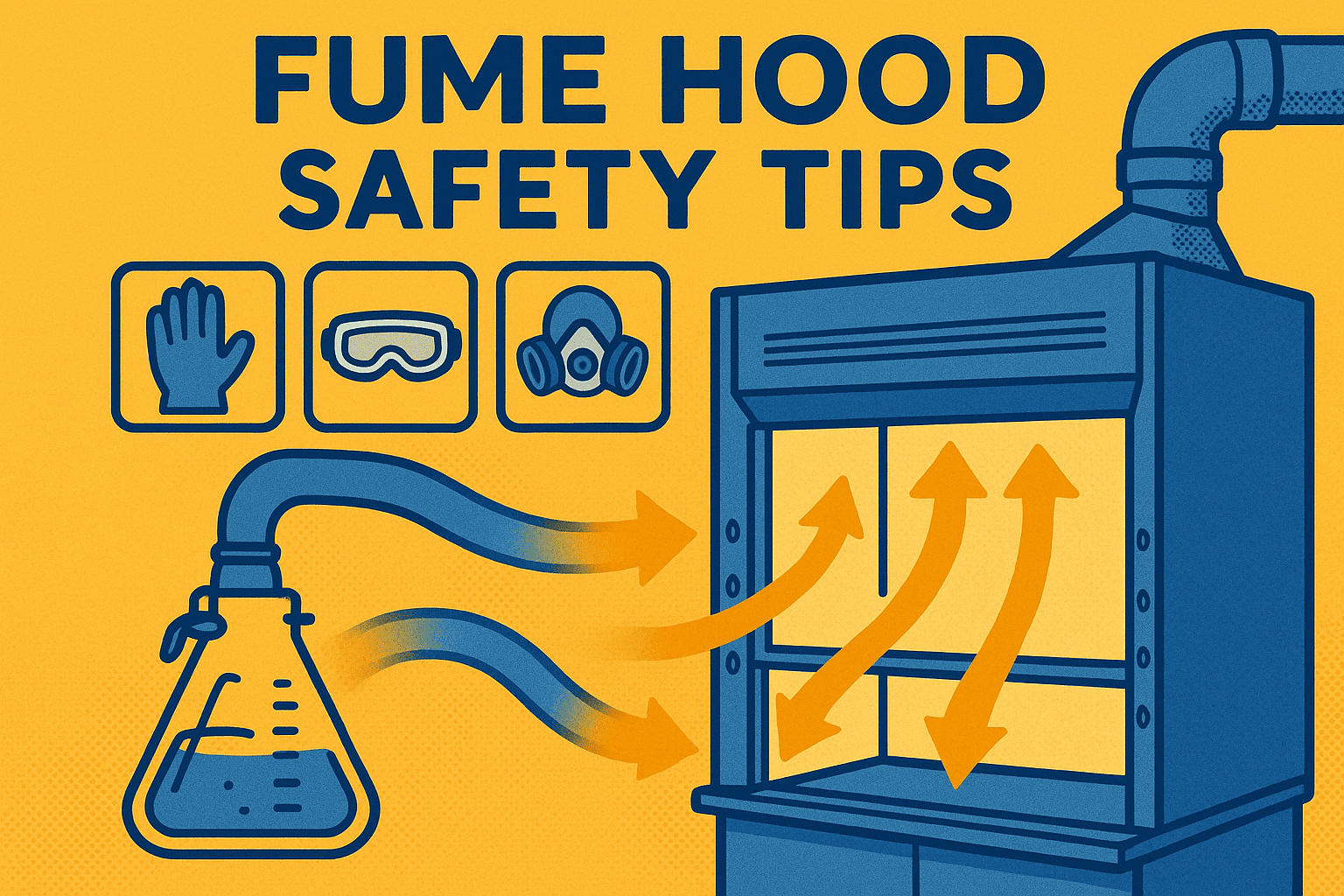
In a lab, safety is non-negotiable. Whether you’re working with toxic fumes or harmful biological agents, having the right equipment matters—a lot. That’s where fume hoods and biosafety cabinets come in. But people often confuse the two. So, let’s break it down in plain English: what’s the difference between a fume hood and a biosafety cabinet?
What is a Fume Hood?
Definition and Basic Purpose
A fume hood is like a vacuum for chemical vapors. It pulls dangerous fumes away from you, so you don’t breathe them in. Simple, right?
Ducted Fume Hoods
These hoods push air through a duct and release it outside the building. Best for strong or toxic chemicals.
Ductless Fume Hoods
These have filters and recirculate clean air back into the room. Great when ductwork isn’t available.
How Fume Hoods Work
Air flows inward from the room and is either filtered or vented outside. You work behind a sash (a sliding glass window) to stay protected.
What is a Biosafety Cabinet?
Definition and Function
A biosafety cabinet (BSC) protects you, your experiment, and the environment. It’s used when you work with viruses, bacteria, and other biological materials.
Class I
Protects the user and the environment, but not the sample.
Class II
Offers protection for all three: user, sample, and surroundings. Most common in biology labs.
Class III
High-level containment. Fully enclosed and airtight—think maximum security.
How Biosafety Cabinets Operate
BSCs filter air through HEPA filters (High-Efficiency Particulate Air). Air flows in a specific pattern to trap harmful agents and avoid contamination.
Key Differences Between Fume Hoods and Biosafety Cabinets
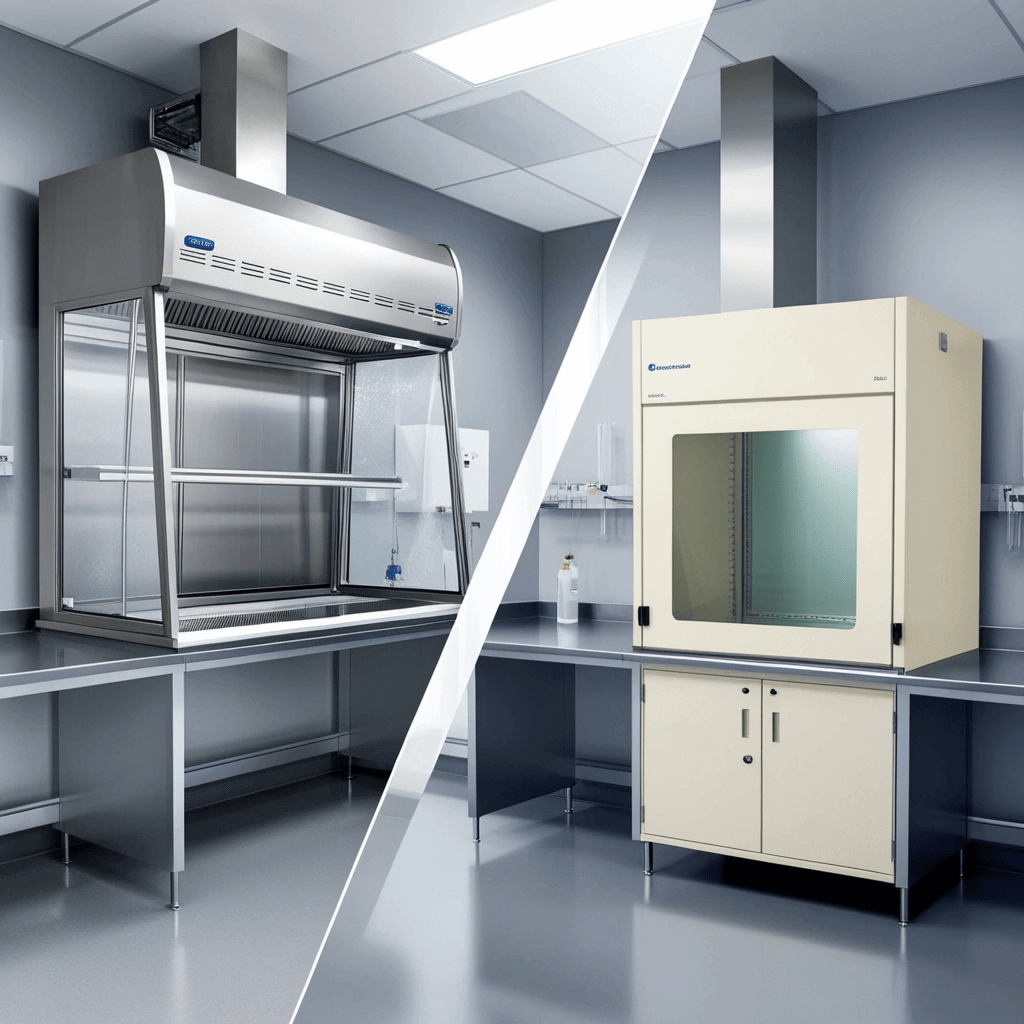
Purpose
- Fume Hood: Protects people from chemical exposure.
- BSC: Protects people, samples, and the environment from biohazards.
Airflow Design
- Fume hoods pull air away from the user.
- BSCs filter and recirculate air inside the cabinet before it’s exhausted.
Protection Level
- Fume hoods = Chemical safety.
- BSCs = Biological safety.
Filtration Systems
- Fume hoods may or may not filter.
- BSCs must have HEPA filters.
When to Use a Fume Hood
Suitable Scenarios
- Mixing acids
- Using volatile solvents
- Chemical reactions with harmful fumes
What Not to Do
- Don’t use it for infectious materials.
- Don’t block airflow with clutter.
When to Use a Biosafety Cabinet
Suitable Scenarios
- Handling bacteria or viruses
- Tissue culture work
- Genetic engineering
Common Mistakes
- Don’t use open flames inside
- Don’t block air grilles
Maintenance and Safety Tips
Fume Hood Maintenance
- Check airflow regularly.
- Replace filters (if ductless).
- Keep sash at the right level.
Biosafety Cabinet Maintenance
- Certify annually.
- Change HEPA filters as needed.
- Clean surfaces with disinfectant.
Final Thoughts
Knowing the difference between a fume hood and a biosafety cabinet isn’t just about terminology—it’s about safety. Use the right tool for the job, and you’ll be protecting more than just your experiment—you’re protecting yourself and everyone around you.
Conclusion
Fume hoods and biosafety cabinets both play a critical role in lab safety, but they’re designed for different tasks. If you’re dealing with chemicals, go with the fume hood. Working with bacteria? Then the biosafety cabinet is your go-to. Understanding the difference helps you make smarter, safer choices in the lab.
FAQs
- What is the main function of a fume hood?
To protect users from inhaling harmful chemical fumes by venting them away. - Can a biosafety cabinet replace a fume hood?
Nope! A BSC is for biohazards, not chemicals. Each serves its own unique purpose. - How often should these units be inspected?
At least once a year, but airflow and filters should be checked regularly. - What’s the difference in cost?
Biosafety cabinets are generally more expensive due to their advanced filtration and design. - Do both protect the user from chemicals?
Only fume hoods are designed for chemical protection. BSCs are not suitable for chemical vapors.