When setting up a modern laboratory, one of the most important investments is a fume hood. This essential equipment ensures a safe, clean, and controlled environment by removing harmful gases, vapors, and particulates generated during experiments. Whether you are designing a research facility, pharmaceutical lab, or academic institution, this fume hood guide will help you make an informed decision.
In this article, we’ll explore the types of fume hoods, key safety tips, and a complete installation checklist — so your laboratory is compliant, efficient, and safe for all users.
1- Understanding the Purpose of a Fume Hood
A fume hood is a ventilated enclosure designed to protect users from inhaling toxic fumes, vapors, and dust. It acts as a barrier between the laboratory personnel and hazardous materials, maintaining a controlled airflow that captures contaminants and expels them safely through an exhaust system.
The primary goal of a fume hood is to enhance chemical lab safety while improving air quality and minimizing exposure risks. Properly installed and maintained fume hoods are a critical component of lab ventilation, ensuring compliance with global safety standards and local regulations.
2- Types of Fume Hoods
Before purchasing, it’s crucial to understand the various types of fume hoods available in the market. Your choice will depend on your laboratory’s specific processes, space, and safety needs.
1- Ducted Fume Hoods
These are the most common and reliable type of fume hoods. They are connected to a building’s external exhaust system, which removes contaminated air completely from the lab.
- Ideal for heavy chemical usage.
- Requires professional installation and ductwork.
- Provides consistent performance and high safety levels.
2- Ductless (Recirculating) Fume Hoods
Ductless fume hoods filter the contaminated air through activated carbon or HEPA filters and then recirculate clean air back into the lab.
- Energy-efficient and flexible.
- Best for light chemical work or mobile setups.
- Requires regular filter replacement and maintenance.
3- Walk-in (Floor-Mounted) Fume Hoods
These large enclosures accommodate bulky equipment or large experimental setups.
- Commonly used in industrial and pilot-scale labs.
- Require spacious rooms and strong ventilation systems.
4- Specialty Fume Hoods
Designed for specific tasks such as radioactive materials or perchloric acid, these hoods feature customized materials and exhaust systems for maximum protection.
Each type serves unique purposes, and choosing the right one will depend on your operational requirements, available space, and chemical lab safety protocols.
3- Factors to Consider Before Buying a Fume Hood
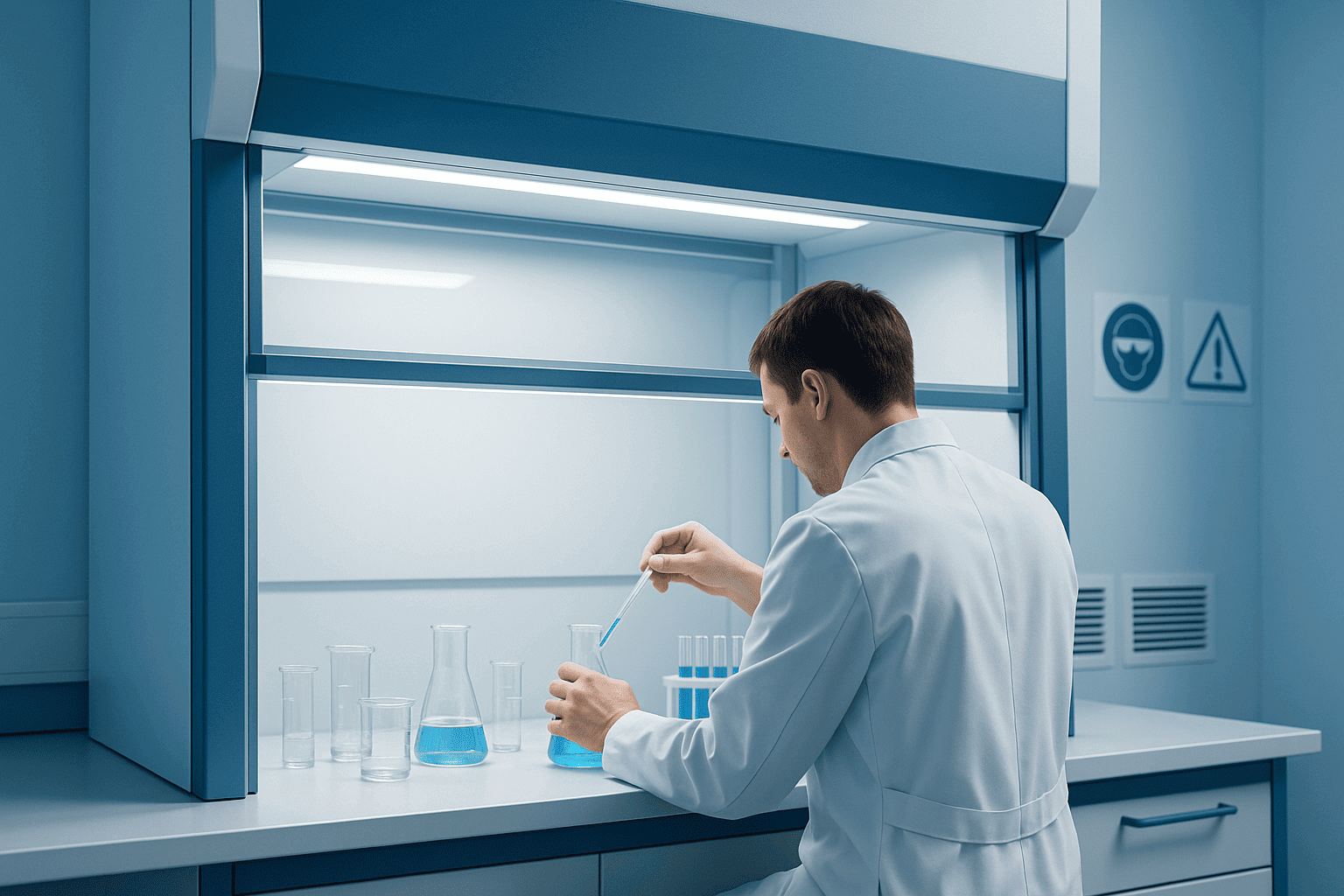

When selecting a fume hood, careful evaluation of several factors ensures long-term safety and efficiency.
1- Airflow and Performance
The hood’s airflow velocity determines its effectiveness. Ensure that face velocity (air entering the hood) meets the standard range of 80–120 feet per minute for most applications.
2- Material and Build Quality
Opt for corrosion-resistant materials such as epoxy-coated steel or polypropylene, depending on the chemicals being handled.
3- Energy Efficiency
Look for models with variable air volume (VAV) systems or energy-saving modes to reduce electricity consumption.
4- Ergonomic Design
Features like adjustable sash height, adequate lighting, and spacious work areas enhance user comfort and safety.
5- Certification and Compliance
Always choose hoods that comply with international standards such as ASHRAE 110 or EN 14175. Check for quality assurance from trusted manufacturers.
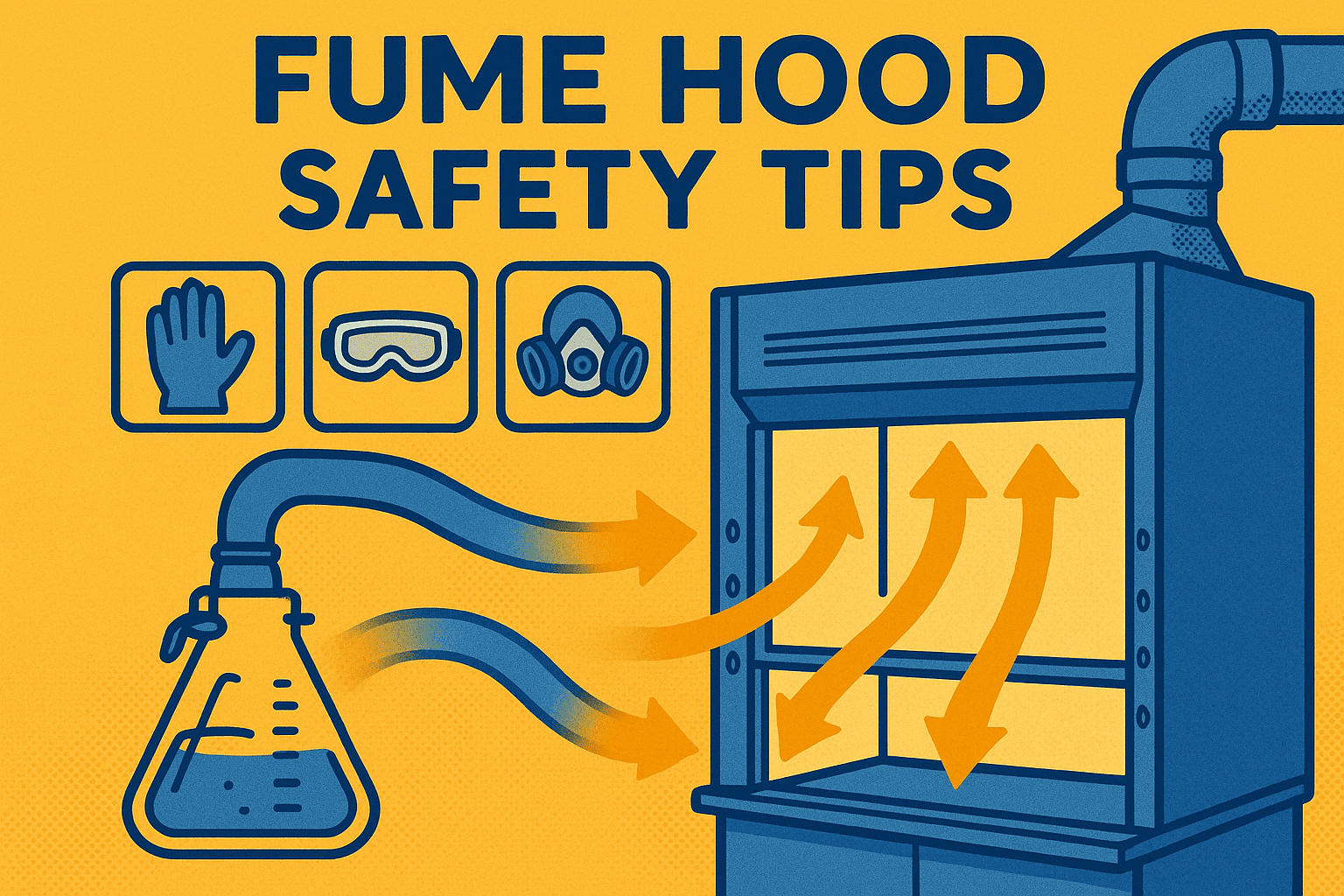
4- Safety Tips for Fume Hood Operation
Even the best fume hood cannot guarantee safety if not used properly. Here are key operational tips to maximize protection:
1- Keep the Sash at the Recommended Height: Operate with the sash partially closed to maintain optimal airflow and minimize exposure.
2- Avoid Storing Chemicals Inside: Fume hoods are for active experiments, not long-term storage. Keeping bottles inside can restrict airflow and create hazards.
3- Perform Regular Maintenance: Clean the surfaces, check the airflow, and schedule periodic inspections.
4- Minimize Air Turbulence: Avoid sudden movements or placing large objects near the hood’s opening, as this can disrupt airflow patterns.
5- Use Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear lab coats, gloves, and safety goggles while working inside the hood.
Following these steps ensures maximum chemical lab safety and prolongs the life of your equipment.
5- Fume Hood Installation Checklist
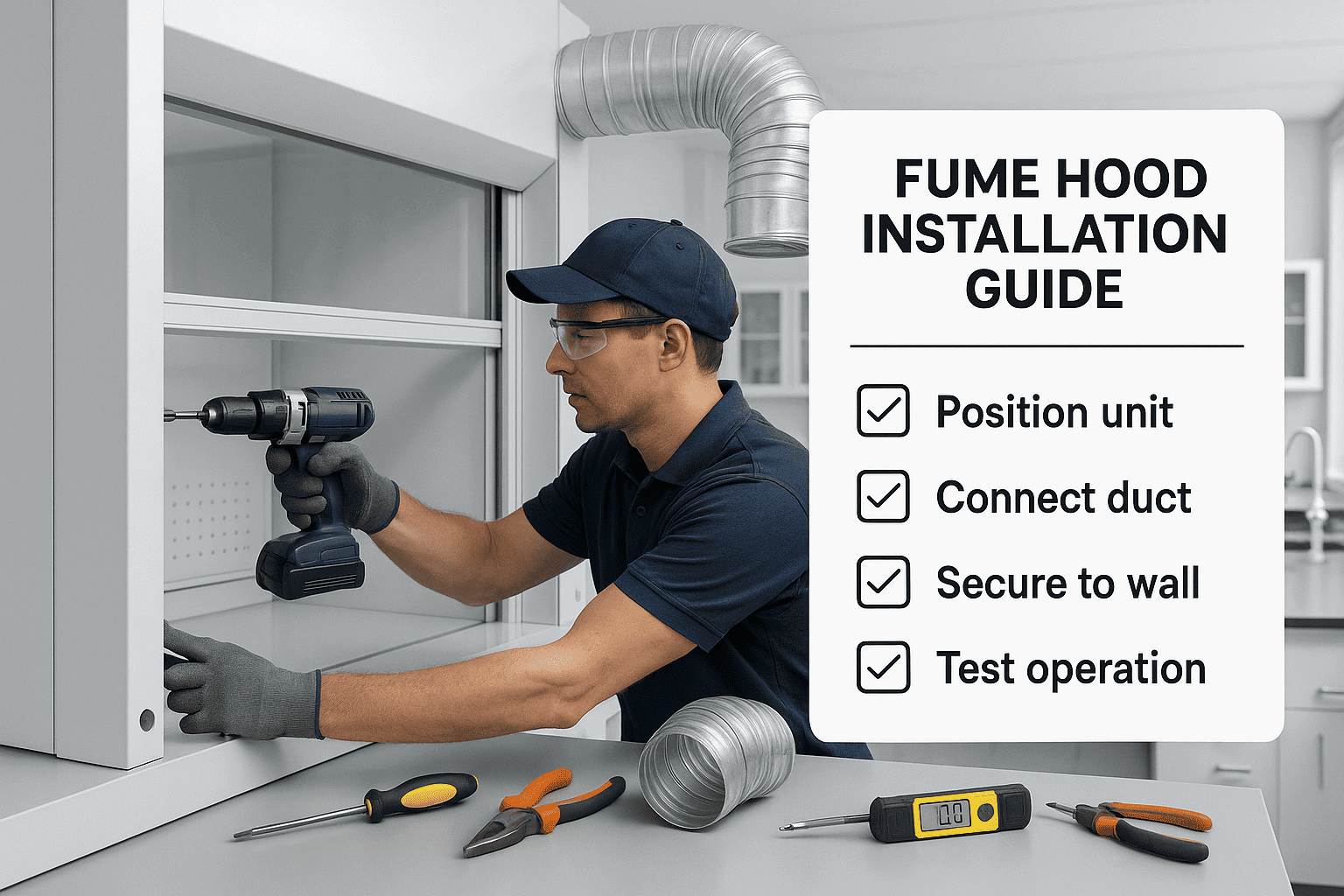
Installing a fume hood requires careful planning and expert supervision. Below is a detailed checklist to guide your installation process:
✅ Pre-Installation Planning
- Assess the laboratory layout and airflow direction.
- Identify the nearest exhaust point or design a duct path.
- Confirm sufficient ceiling height and spacing for ductwork.
- Obtain necessary building and safety approvals.
✅ During Installation
- Position the fume hood away from doors, windows, and high-traffic areas to prevent airflow disturbances.
- Ensure all duct connections are sealed properly.
- Verify that electrical and plumbing services (if required) are safely integrated.
- Install appropriate lighting and safety alarms (airflow monitors).
✅ Post-Installation Validation
- Conduct airflow tests and verify exhaust performance.
- Calibrate the face velocity according to manufacturer recommendations.
- Provide staff training on correct operation and maintenance procedures.
- Schedule routine inspection and certification checks every 6–12 months.
Following this fume hood guide helps you ensure safe, reliable, and efficient setup for any laboratory environment.
6- Maintenance and Periodic Testing
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the long-term performance of your fume hood.
- Inspect filters (for ductless models) and replace them as needed.
- Check airflow alarms and monitor calibration regularly.
- Schedule preventive maintenance with professional service providers to avoid costly downtime.
Leading laboratory solution providers such as chameza.in, labturnkey.in, and labcreator.in offer certified installation, testing, and maintenance services to ensure compliance with safety standards. Partnering with experienced professionals ensures that your lab remains functional, compliant, and hazard-free.
7- Conclusion
A fume hood is more than just equipment — it’s a safety shield that protects researchers, ensures compliance, and maintains clean air quality in your workspace. By understanding the different types of fume hoods, following proper safety tips, and implementing a reliable installation checklist, you can create a safe and efficient laboratory environment.
Investing wisely today prevents costly incidents tomorrow. When planning your lab setup, always prioritize performance, safety, and certification — because when it comes to laboratory safety, prevention is far more valuable than correction.
Whether you’re setting up a small academic lab or a large industrial research center, let this fume hood guide serve as your trusted companion in building a secure, compliant, and sustainable workspace supported by strong lab ventilation and chemical lab safety practices.